Grading in U.S. public schools isn’t universal. A 93% might mean an A in one state and a B in another—because grading scales vary by state, district, and even grade level.
As GPA targets, college admissions, and academic standards evolve in 2024–2025, it’s more important than ever to understand how your state calculates grades. Whether you’re a student, a parent decoding report cards, or an educator comparing policies, knowing how your local system works is essential.
This guide breaks it all down for you:
✅ A state-by-state breakdown of letter grade conversions
✅ What newer grading approaches like competency-based learning mean for students
✅ How standardized testing and GPA calculations factor into the bigger picture
No guesswork—just a clear overview of what grades mean where you are.
Plus, if you’re calculating your GPA, don’t miss our detailed breakdown of the weighted vs. unweighted GPA—so you know exactly what counts and why.
Stay informed. Understand how grading works in your state.
Some families are choosing hybrid high schools—combining online flexibility with in-person days—and it’s worth seeing how their grading systems compare.
I’d recommend checking out our Best Hybrid High Schools (Online + In-Person) in the U.S. guide to explore real examples and what to expect.
Understanding Public School Grading Scales in the U.S.
Understanding how grading scales impact school rankings is essential when exploring the Best U.S. High Schools.
Grading scales are an essential part of the educational system, determining how students’ academic performance is evaluated. In the U.S., these scales vary widely from state to state, and in 2024, some states have even introduced new grading methods that may impact students significantly.
What is a Grading Scale?
A grading scale is a system that assigns a letter grade (like A, B, C, etc.), percentage, or GPA to a student’s performance in their coursework. These grades reflect how well a student understands the material and meets the course requirements.
Common Grading Systems in the U.S.:
- Letter Grades (A-F): The most traditional grading system where A is the highest grade and F represents failure.
- Percentage Scores: Often used alongside letter grades, where a percentage score corresponds to a letter grade (e.g., 90-100% = A).
- GPA (Grade Point Average): A cumulative score typically on a 4.0 scale that averages a student’s grades over time.
Example of a Basic Grading Scale:
| Letter Grade | Percentage Range | GPA |
|---|---|---|
| A | 90-100% | 4.0 |
| B | 80-89% | 3.0 |
| C | 70-79% | 2.0 |
| D | 60-69% | 1.0 |
| F | 0-59% | 0.0 |
Confused about how your grades affect your GPA?
👉 Read our complete guide on Understanding GPA — learn how letter grades turn into a GPA score and why it matters.
Recommended Prep Books for GPA Boosters (2025 Edition)
A strong GPA is great — but top colleges also look at SAT/ACT scores to measure academic readiness. Here are three standout test prep books for 2025 to help students improve both their grades and college prospects:
( Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links. If you click and make a purchase, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we truly believe help students succeed.)
1. The Official SAT Study Guide 2025 Edition
- From: College Board (official test makers)
- Features: 8 real, full-length practice tests + answer explanations
- Best for: Students aiming for authentic practice and accuracy
2. Kaplan SAT Prep Plus 2025
- What’s inside: 5 full-length tests, online quizzes, and video lessons
- Why it helps: Strategy-based coaching, great for visual learners
- Ideal for: Students targeting a 1200–1500+ SAT score
3. Barron’s ACT Premium Study Guide 2025
- From: Barron’s Educational Series
- Includes: 8 full-length practice tests (4 in-book, 4 online)
- Standout Features: In-depth answer explanations, online practice, and review for all ACT sections (English, Math, Reading, Science, and Writing)
- Best for: High achievers or students who want both content mastery and realistic practice
✅ Pro Tip: Use these books alongside a GPA planner or prep schedule. A consistent test-prep routine can raise both GPA and admission chances.
Whether you’re aiming for an A or trying to move from a B to an A-, the right study tools can make a real difference. See the 25+ Best Study Tools for Students →
Variations Across States
While the basic grading scale is fairly consistent, the details can vary depending on the state and even individual school districts.
Regional Differences
- Northeast: Some states like New York have adopted more stringent grading scales where a score below 65% is considered failing.
- South: In states like Florida, there may be a larger range for passing grades, and certain schools use a weighted GPA system to reflect advanced coursework.
These differences can significantly affect how a student’s academic performance is viewed, especially when applying for colleges or scholarships.
Wondering how your grades stack up with test scores? Check out the PSAT score ranges explained
Recent Changes in 2025: What You Should Know
Grading policies aren’t set in stone—and 2024 proves just that. As schools continue to adapt to evolving learning needs, several states have updated how they assess and report student performance.
- California has introduced more flexibility in grading, giving schools room to consider things like project-based learning and student growth over time. This shift helps accommodate different learning styles and makes room for a more holistic view of progress.
- Texas, on the other hand, has revised its GPA calculation methods, putting more weight on advanced courses like AP and honors classes. For students aiming for competitive college applications, this could have a meaningful impact on transcripts.
These updates reflect a growing awareness that one-size-fits-all grading doesn’t always work—and that academic systems need to evolve with students, not just test them. If you’re a parent or student navigating these changes, knowing what’s new can help you make more informed decisions.
✅ Tip: Always check with your school or district for the latest grading policies—they may adopt changes at different times or apply them in unique ways.
For families prepping for college admissions, investing in top-rated tools like the Barron’s SAT Study Guide Premium 2025 can make a big difference.
While GPA is important, colleges also value skills and certifications. If you’re aiming to strengthen both, [Coursera’s academic success and study skills programs] are a great starting point.
Regional Grading Differences in 2024-2025
Grading scales vary widely across the U.S.—and in 2025, that’s more true than ever. Some states use traditional letter grades, while others are shifting toward flexible, skills-based models.
For students switching schools or families relocating, these regional differences can affect transcripts, GPA, and college readiness. This section highlights key grading trends by region to help you understand how each area measures student success.
Northeast States: High Standards, Tight Grading
Schools in the Northeast often uphold strict academic expectations, and that shows in their grading scales. Many states in this region stick to traditional percentage cutoffs, with fewer leniencies for borderline grades. This reflects the region’s strong focus on academic rigor and college preparation.
Grading in New York: What to Expect
Most New York schools use a 100-point scale, where an A starts at 90%. Advanced courses like AP and Honors are weighted, giving students a GPA boost for more rigorous classes. A key feature of New York’s system is the Regents Exams, which heavily influence high school grades and graduation eligibility.
Here’s a table for New York’s typical grade breakdown along with AP course weighting adjustments for GPA:
| Grade | Percentage Range | Standard GPA Points | Weighted GPA Points (AP/Honors) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A+ | 97-100 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
| A | 93-96 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
| A- | 90-92 | 3.7 | 4.7 |
| B+ | 87-89 | 3.3 | 4.3 |
| B | 83-86 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| B- | 80-82 | 2.7 | 3.7 |
| C+ | 77-79 | 2.3 | 3.3 |
| C | 73-76 | 2.0 | 3.0 |
| C- | 70-72 | 1.7 | 2.7 |
| D+ | 67-69 | 1.3 | 2.3 |
| D | 65-66 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| F | Below 65 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
Key Notes:
Variations Across Districts: Some districts may have slightly different percentage ranges or weighting systems, so it’s always best to check with local school policies.
Weighted GPA: For AP or Honors courses, schools add an additional 1.0 point to the GPA calculation to reward the increased difficulty level.
Stat: In 2023, 85% of New York high school students passed at least one Regents exam.
Not all GPAs are created equal!
👉 Discover the difference between weighted and unweighted GPA — especially important for honors and AP students.
Grading in Massachusetts: High Standards and Testing Weight
Massachusetts uses a 100-point scale, but schools often set a higher bar—an A typically starts at 93%, unlike the more common 90% threshold in other states.
The state’s grading approach places strong emphasis on the MCAS (Massachusetts Comprehensive Assessment System), a standardized test that can significantly impact both student report cards and school rankings.
Did you know? Massachusetts was ranked #1 in education performance in 2023 (Education Week, Quality Counts report).
Here’s how MCAS-based grading compares to traditional assessments:
| Category | MCAS Weightage in Grading | Traditional Assessments |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures student proficiency on state standards and readiness for next grade. | Evaluates understanding of material taught in a specific course. |
| Weight in Final Grade | Typically accounts for 10-25% of a student’s final grade in key subjects (varies by district). | Weight is determined by teachers and often based on classroom tests, homework, and participation. |
| Assessment Type | Standardized, state-administered tests in subjects like Math, English, and Science. | Classroom-based tests, quizzes, projects, and assignments. |
| Frequency | Administered once a year (spring). | Occurs throughout the school year. |
| Content Focus | Focuses on core subjects aligned to Massachusetts Curriculum Frameworks. | Varies based on the teacher’s curriculum and course objectives. |
| Feedback Timeline | Results are available months after testing. | Feedback is typically provided within days or weeks. |
| Impact | Results may influence district rankings, teacher evaluations, and student graduation eligibility. | Primarily impacts student grades for a specific course. |
| Customization | Standardized for all students in the state, with no customization. | Tailored to the class curriculum and teaching style. |
| Skill Measurement | Focuses on critical thinking, problem-solving, and mastery of state standards. | May include rote learning, memorization, or specific skills relevant to the class. |
| Transparency | Grading criteria are uniform and published by the state. | Grading criteria may vary significantly across schools and teachers. |
How MCAS Results Impact Students
MCAS scores influence key aspects of a student’s academic journey in Massachusetts:
Support and Opportunities: Poor results trigger remediation, while high scores can open doors to scholarships, like the John and Abigail Adams Scholarship, and placement in advanced programs.
Grade Advancement: Low performance, especially in critical years like middle-to-high school transitions, may require remediation programs or additional support before promotion.
Graduation Requirement: To graduate high school, students must meet the state’s minimum passing scores in ELA, Math, and Science.
Students below this threshold may need to retake exams or complete a tailored educational proficiency plan (EPP).
👉 Looking to understand how Advanced Placement (AP) courses impact your GPA? Our guide on AP Exam Scoring & How It Affects Your GPA explains how AP scores contribute to weighted GPAs and college admissions.
If your student is in AP or Honors courses, consider the Barron’s AP Review Books—comprehensive and regularly updated for each subject.
Midwest States
The Midwest region has a more standardized approach, with many states sticking to traditional grading methods but also experimenting with new policies.
Grading Scales in Illinois
Illinois schools frequently use the 4.0 GPA scale, where an ‘A’ equals 4.0 points. In urban areas, a plus/minus grading system (e.g., B+ = 3.3, B = 3.0) adds more precision to grading.
Schools in Illinois are increasingly incorporating competency-based education models, especially in pilot programs, which aim to measure skill mastery rather than traditional grades.
Stat: As of 2024, 10% of Illinois districts have adopted competency-based education frameworks.
Comparison: Traditional GPA vs. Competency-Based Grading in Illinois
| Criteria | Traditional GPA Grading | Competency-Based Grading |
|---|---|---|
| Grading Focus | Performance on tests, assignments, and participation contribute to the final grade. | Focuses on mastering specific skills or competencies outlined in the curriculum. |
| Scoring System | Grades are based on a letter scale (A = 4.0, B = 3.0, etc.). | Students are rated on proficiency levels (e.g., Emerging, Developing, Proficient, Advanced). |
| Example Grade Representation | A: 90–100%, B: 80–89%, C: 70–79%, etc. | Proficient: Mastery of 80%+ of the skill; Developing: Partial understanding but progressing. |
| Assessments | Cumulative grades from tests, homework, and projects. | Students demonstrate mastery through multiple attempts and varied assessments. |
| Learning Pace | All students progress together based on the school year schedule. | Students progress at their own pace, advancing only when they’ve mastered the material. |
| Retakes/Redos | Rarely allowed; penalties may apply for late submissions. | Encouraged to ensure mastery, with no penalties for retaking assessments. |
| Example Report Card | GPA: 3.5 (A-, B+, A in different subjects). | Competency Levels: Math – Proficient, Science – Developing, Language Arts – Advanced. |
| Purpose | Focus on ranking students and preparing for college admissions. | Focus on skill acquisition, personalized learning, and preparing for real-world application. |
Discover everything you need to know about competency-based grading in our Comprehensive Guide to Competency-Based Grading.
Grading Scales in Ohio
Ohio schools generally use a system similar to Illinois but with less focus on plus/minus grading distinctions.
Recent updates in 2024 introduced more holistic assessment methods, including teacher evaluations that consider classroom participation and effort alongside test scores.
Ohio also emphasizes End-of-Course (EOC) exams, which affect final grades in core subjects like Algebra and English.
Stat: In 2023, Ohio reported a 5% increase in high school graduation rates due to updated grading practices.
| State | Grade A (GPA) | Use of Plus/Minus | Recent Changes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Illinois | 4.0 | Yes | Urban schools favor more detail |
| Ohio | 4.0 | No | Introduction of holistic assessment |
Southern States
The South sees a mix of traditional and modern approaches, often reflecting the educational priorities of each state.
Grading Scales in Texas
Texas employs a 100-point grading scale, with an ‘A’ typically beginning at 90%. The state places significant weight on STAAR (State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness) standardized tests, which influence student progression and school accountability. Many Texas districts also weight GPAs for AP, Dual Credit, and Honors courses.
Stat: In 2023, over 70% of Texas students were enrolled in at least one advanced course, such as AP or Dual Credit.
Grading Scales in Florida
Florida follows a 4.0 GPA system but is increasingly adopting competency-based education models. This approach allows students to progress by demonstrating mastery of skills rather than meeting arbitrary grade thresholds.
These reforms aim to reduce the emphasis on standardized testing and foster personalized learning experiences.
Stat: By 2024, over 50% of Florida schools implemented competency-based education in some capacity.
| State | Grade A Range | GPA System | Educational Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Texas | 90-100 | 4.0 | High weight on standardized tests |
| Florida | 90-100 | 4.0 (shifting to competency-based) | Mastery over grades |
Want to see your actual GPA from your grades?
- Letter to GPA Converter Tool
- Cumulative GPA Calculator
- Final Grade Calculator
Use these tools to plan smarter!
Western States
The Western U.S. often leads in educational innovation, with states like California and Washington frequently updating their grading systems to reflect new educational philosophies.
Grading Scales in California
California schools primarily use the 4.0 GPA system but are moving towards narrative evaluations alongside traditional grades.
Narrative evaluations provide detailed feedback on a student’s strengths and areas for improvement, especially in middle and high schools.
California’s emphasis on equity in grading has led many districts to eliminate penalties for late work and encourage retakes on assessments.
Stat to Add: By 2023, over 60% of California school districts had adopted alternative grading practices.
Grading Scales in Washington
Washington has adopted standards-based grading in many districts, where students are graded on their mastery of specific learning standards rather than cumulative scores.
This approach provides more transparency for students and parents, as it focuses on skill acquisition instead of test performance.
Stat: As of 2024, 75% of Washington districts reported using standards-based grading in at least one grade level.
| State | GPA System | Innovative Practices | 2024 Updates |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | 4.0 | Narrative evaluations, especially in high schools | Incorporation of soft skills in grading |
| Washington | Standards-based | Grading on standards rather than scores | Expanded use of standards-based grading |
U.S. Grading Scale Comparison Chart
To help visualize these differences, here is a chart comparing grading scales across the regions:
| Region | Common Grading System | Notable Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Northeast | 100-point scale | Strong emphasis on academic rigor |
| Midwest | 4.0 GPA scale | Introduction of holistic assessments |
| South | Mix of 100-point and 4.0 GPA | High weight on standardized testing |
| West | 4.0 GPA/Standards-based | Emphasis on innovative grading practices |
This regional analysis highlights how diverse grading practices can be across the U.S.
As the landscape of public education continues to evolve, staying informed about grading scale changes is crucial for students, parents, and educators.
These adjustments not only reflect shifting educational priorities but also have significant implications for academic progression and future opportunities.
By understanding the regional differences and recent updates in 2024, stakeholders can better navigate the complexities of the U.S. education system.
If you plan to homeschool your child, follow our guide and read the post Homeschool Grading Systems: Customization, Tools, and State-Specific Requirements.
Interactive Comparisons of Grading Scales
When comparing public school grading scales across U.S. states, it’s easy to get lost in numbers and letter grades.
To help you understand these differences, let’s break it down using tables, charts, and visual aids. This way, you can quickly compare each state’s system at a glance.
Grading Scale Table by U.S. Region
Here’s a simple table that outlines the general grading scale for several states across different regions of the U.S. in 2024:
| Region | State | A Grade | B Grade | C Grade | D Grade | F Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northeast | New York | 90-100% | 80-89% | 70-79% | 65-69% | Below 65% |
| Midwest | Illinois | 93-100% | 85-92% | 77-84% | 70-76% | Below 70% |
| South | Texas | 90-100% | 80-89% | 70-79% | 60-69% | Below 60% |
| West | California | 90-100% | 80-89% | 70-79% | 60-69% | Below 60% |
- ✅ Quickly find percentage scores without a calculator!
Teachers love the EZ Grader for fast and accurate test grading.
Get the EZ Grader on Amazon
This table helps you quickly identify how each state assigns letter grades based on percentage.
Notice the small differences—like Illinois having a slightly higher threshold for an A compared to other states. These details can be critical for students moving between states or applying to colleges.
While public schools widely use traditional grading scales like letter grades and percentages, many educators are exploring how alternative systems can provide a more holistic approach to evaluate student performance.
Key Takeaways from State-by-State Grading Comparisons
It matters for planning: Whether you’re relocating or applying to colleges, knowing how grades are calculated across states helps students and parents make smarter academic decisions.
Grading standards vary widely: Some states, like Illinois and Texas, have higher cutoffs for top grades, which can influence GPA and college admissions.
Regional similarities exist—but don’t assume: While nearby states often share grading trends, important differences still exist—even within the same region.
Trying to improve your GPA this year?
We’ve tested 25+ of the best study tools and resources (including AI apps, flashcard generators, and Chrome extensions) that actually help students get better grades.
👉 Check them out here →
Just like grading scales can affect how colleges view your transcript, your writing style—such as using active vs. passive voice—can also influence application essays.
FAQs on Grading Scale
How many schools have an A grade in 2024?
While the exact number of schools with an A grade in 2024 varies by state, education agencies like Florida’s Department of Education often report school performance annually. For example, in previous years, around 30-35% of Florida schools received an A, but the numbers for 2024 are still being updated.
How many grades are there in the US grading system?
The most common letter grading system in the U.S. includes five primary grades: A, B, C, D, and F. Some schools also use pluses and minuses (e.g., A-, B+), creating a finer distinction in performance. These grades typically correspond to a percentage range (e.g., A = 90-100%, B = 80-89%).
Tip: Always check the specific school’s grading policy as it can vary by district, and some may include unique grading systems like pass/fail or competency-based assessments.
What is a GPA grading scale?
A GPA (Grade Point Average) is a numerical representation of a student’s academic performance, usually on a 4.0 scale where A = 4.0, B = 3.0, and so on. Some schools also use weighted GPAs (up to 5.0) to give extra credit for honors or AP courses. It averages the grades across all courses a student has taken, offering a summary of their overall academic achievement.
Tip: Focus on improving your GPA by targeting weaker subjects with tutoring or extra credit opportunities to ensure a strong academic transcript.
How many Florida charter schools have an A grade in 2024?
As of 2024, the specific number of charter schools with an A grade in Florida is subject to state reporting, typically released after performance reviews. In recent years, around 40-45% of Florida charter schools have achieved an A grade. High-performing charter schools often emphasize smaller class sizes, innovative curriculum models, and strong parental involvement.
Tip: For a charter school aiming to achieve or maintain an A grade, focus on community engagement and regular progress assessments to align with state standards.
What grading system does the US use?
The U.S. uses a letter grading system (A-F), where A represents excellent performance and F indicates failing. It often aligns with a percentage scale (e.g., A = 90-100%). Some schools also employ a GPA system to aggregate performance across subjects. Additionally, other systems like pass/fail or competency-based grading are increasingly used in alternative educational settings.
Tip: Schools moving toward competency-based grading should focus on mastery of skills rather than standardized tests, encouraging deeper learning and long-term retention.
What is the scale for grades?
The grading scale typically converts percentages into letter grades. A common scale in the U.S. looks like this:
A: 90–100%
B: 80–89%
C: 70–79%
D: 60–69%
F: Below 60%
💡 Tip: Some schools use a weighted system where honors or AP courses give extra points, making an “A” worth more
Is 70% a grade A?
No, a 70% is usually a C on the standard grading scale. To get an A, you’d need at least 90%.
Insight: Some schools curve grades or have customized scales, so always check with your institution’s policy.
What is the 5-point grading scale?
The 5-point grading scale assigns points to letter grades, typically:
5: A (Excellent)
4: B (Good)
3: C (Average)
2: D (Below Average)
1: F (Failing)
Actionable Tip: Use this scale to calculate GPA by dividing the total points earned by the number of classes.
Is 60 or 70 a passing grade?
It depends on the institution, but generally:
60%: Often the lowest passing grade (D).
70%: A solid passing grade (C).
Pro Tip: In professional or licensing exams, 70% is more commonly considered the passing threshold. Always verify for specific scenarios!
Advanced Placement (AP) exams follow a 1–5 scale, which often maps to a weighted GPA scale. See how AP scores can shift your GPA.
Curious how AP grading compares to IB? This college preference guide breaks it down.
Why Trust This Guide on U.S. Grading Scales?
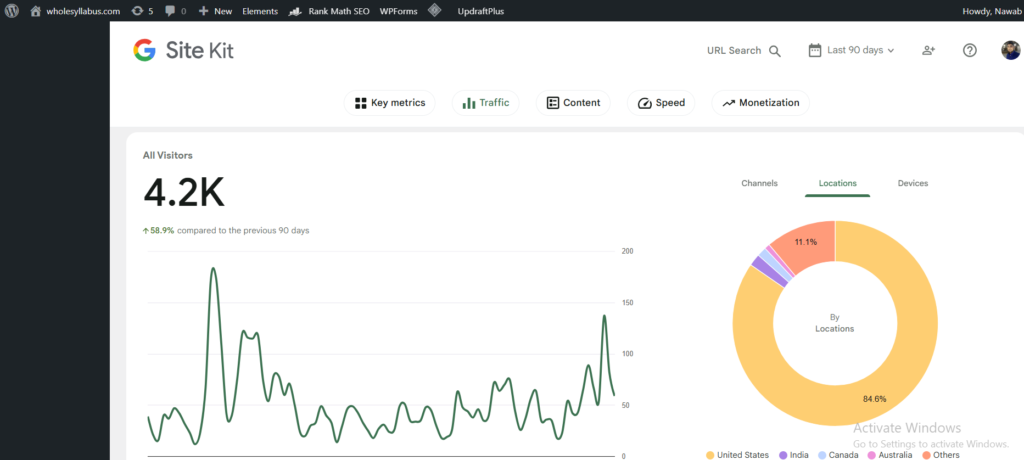
This article is published on Wholesyllabus.com, a trusted U.S.-focused education blog reaching over 4,200+ visitors in the past few days — with 84.6% of our readers from the United States, according to Google Site Kit.
We’re also verified by Bing Webmaster Tools, ensuring our content is visible and credible across major search platforms.
Whether you’re a parent comparing GPA grading systems, a student confused by how school planning affects your transcript, or simply exploring study guides and academic tools, this guide simplifies it all — using official references and real-life insights from Reddit, Quora, and state education boards.
Recommended Coursera Courses
nderstanding grading scales is just one part of the journey. To stay ahead in school and prepare for college, online courses like [Coursera’s Study Skills for Success]can give you a real edge
- Learning How to Learn (perfect fit, highly rated)
- Mindshift: Break Through Obstacles to Learning
- College Success Courses (general prep, time management, study strategies)

Nawab, an educator teaching K-12 since 2010, holds an English honors graduate degree and a diploma in elementary education. He has also been blogging for five years, sharing insights for educators and parents.


5 thoughts on “U.S. Public School Grading Scales 2024-2025: State-by-State Breakdown”