Your Grade Point Average (GPA) is more than just a number—it can shape your path to college, scholarships, internships, and even future jobs. Whether you’re a high school student tracking your progress or a parent trying to understand how GPA systems work, this guide breaks it all down in plain language.
In this all-in-one GPA guide, you’ll learn:
- ✅ What GPA means and how it’s calculated
- ✅ The difference between cumulative, weighted, and unweighted GPA
- ✅ How to use GPA calculators to simplify the math
- ✅ What’s considered a “good” GPA for high school and college
- ✅ GPA scales, conversions, and expert-backed tips to boost your score
Let’s dive in—whether you’re aiming to improve your GPA or just understand how it works, this guide has everything you need.
Did you know? AP exams can actually raise (or lower) your GPA — but only if your school uses weighted grading. Find out how AP scores impact GPA
Quick Facts: Why GPA Matters
- Career Opportunities: A solid GPA on your resume can make a positive impression on recruiters and employers.
- College Admissions: Most universities set minimum GPA requirements for applicants, making it a non-negotiable factor in the application process.
- Scholarships: Many merit-based scholarships rely heavily on GPA to determine eligibility.
New to U.S. schooling? First, check out what K–12 means, grade by grade →
GPA vs Cumulative GPA: What’s the Difference?
GPA and cumulative GPA are closely related—but they’re not the same.
- GPA usually refers to your grade point average for one term, like a semester or quarter.
- Cumulative GPA is your overall GPA across multiple terms, showing your academic performance over time.
Why It Matters
Colleges and scholarship boards often focus more on your cumulative GPA because it reflects your long-term consistency—not just one good (or bad) semester.
SAT scores impact your college readiness — here’s a last-minute SAT guide to complement GPA planning.
Key Difference Table
| Term | What It Includes | When It’s Used |
|---|---|---|
| GPA | Single semester or grading period | Mid-year reports, academic probation, course planning |
| Cumulative GPA | All completed courses to date | College applications, honors programs, final transcripts |
How to Calculate Cumulative GPA (Step-by-Step)
To calculate your cumulative GPA, follow this formula:
Cumulative GPA = (Total Grade Points for All Semesters) ÷ (Total Credit Hours Attempted)
Example: 2-Semester Cumulative GPA
Let’s say you took the following courses:
Semester 1
| Course | Grade | Credits | Grade Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| English | A (4.0) | 3 | 12.0 |
| Math | B+ (3.3) | 4 | 13.2 |
| History | B (3.0) | 3 | 9.0 |
Semester 1 GPA = (12.0 + 13.2 + 9.0) ÷ 10 credits = 3.42
Semester 2
| Course | Grade | Credits | Grade Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biology | A- (3.7) | 4 | 14.8 |
| Chemistry | B (3.0) | 3 | 9.0 |
| PE | A (4.0) | 1 | 4.0 |
Semester 2 GPA = (14.8 + 9.0 + 4.0) ÷ 8 credits = 3.45
Final Cumulative GPA
- Total Grade Points = 12.0 + 13.2 + 9.0 + 14.8 + 9.0 + 4.0 = 62.0
- Total Credits = 10 + 8 = 18
- Cumulative GPA = 62.0 ÷ 18 = 3.44
✅ Your Cumulative GPA after 2 semesters is 3.44
Need a Cumulative GPA Calculator? ➡️Use Tool »
Want a detail guide on Cumulative GPA? Visit here.
How to Calculate GPA: Step-by-Step Guide
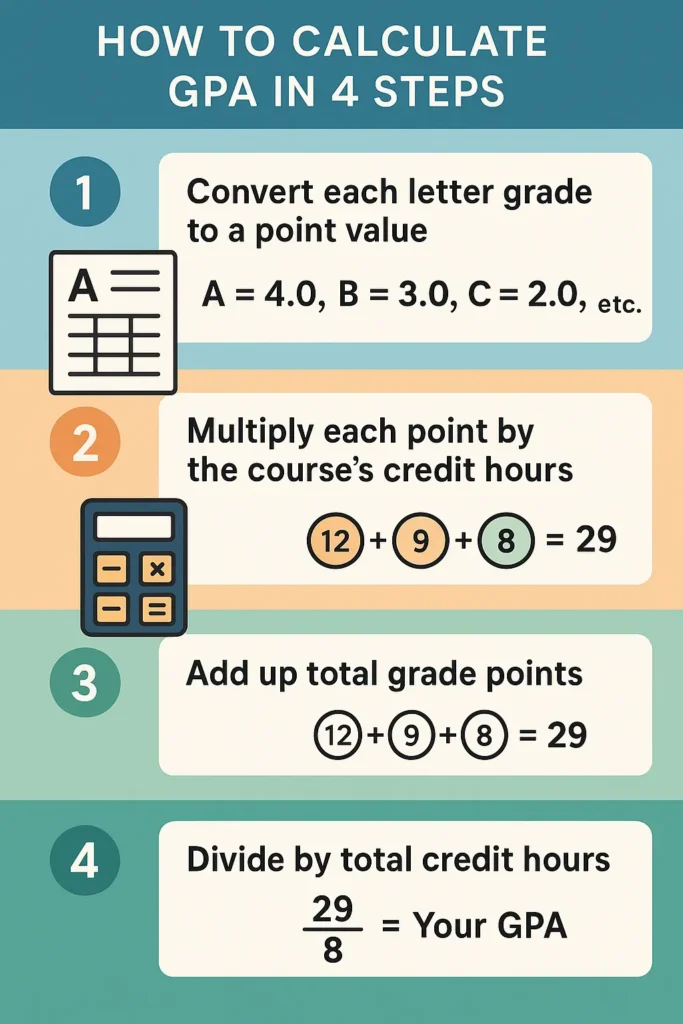
Calculating your GPA might seem tricky at first, but it’s pretty straightforward when broken down into steps. Whether you’re working with an unweighted or weighted GPA, here’s how to do it:
1. Assign Grade Points to Each Class
Each letter grade corresponds to a specific number of grade points. Here’s the standard unweighted scale:
- A = 4.0
- B = 3.0
- C = 2.0
- D = 1.0
- F = 0.0
For a weighted GPA, advanced courses like AP or honors may add extra points:
- A in AP/Honors = 5.0 (instead of 4.0)
- B in AP/Honors = 4.0 (instead of 3.0)
2. Multiply Grade Points by Credit Hours
Some classes, like core subjects, may carry more credit hours. Multiply the grade points by the number of credits for each class. For example:
- An A (4.0) in a 3-credit class = 4.0 × 3 = 12 points
- A B (3.0) in a 2-credit class = 3.0 × 2 = 6 points
3. Add Up Total Grade Points
Add the grade points from all your classes. For instance:
- Class 1: 12 points
- Class 2: 6 points
- Class 3: 8 points
- Total: 26 points
4. Divide by Total Credit Hours
Finally, divide the total grade points by the total credit hours to get your GPA. If your total grade points are 26 and total credits are 7:
- GPA = 26 ÷ 7 = 3.71
How Grades Like A+ or A- Affect GPA
Letter grades like A+ and A- can fine-tune your GPA. Here’s how they typically work:
- A+ = 4.3 (on some scales)
- A- = 3.7
- B+ = 3.3
- B- = 2.7
For example, if you earn an A- in a 3-credit class:
- Grade Points = 3.7 × 3 = 11.1
Small differences like these can add up, especially when calculating GPAs over several semesters or in competitive environments like college admissions.
If you’re unsure how to translate letter grades into GPA points, try this letter grade to GPA converter tool.
Watch: How to Calculate GPA in 60 Seconds
Use our final grade calculator to see what you need on your next exam.
GPA Scales & Conversion Charts
Understanding how GPA is calculated starts with knowing the grading scale your school uses. While many U.S. high schools and colleges use a 4.0 scale, some apply weighted systems or percentage-based scales. Here’s how they compare:
Your PSAT score is often the first big test score that connects to GPA planning — check out our PSAT 2025 Guide
Standard 4.0 Scale (Unweighted)
| Letter Grade | Percent Range | GPA Value |
|---|---|---|
| A | 90–100% | 4.0 |
| B | 80–89% | 3.0 |
| C | 70–79% | 2.0 |
| D | 60–69% | 1.0 |
| F | Below 60% | 0.0 |
This is the most common grading scale used in unweighted GPA calculations.
Weighted 5.0 Scale (for Honors, AP, or IB Classes)
Some schools add extra points to more challenging courses:
| Letter Grade | Regular Class | Honors | AP/IB |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 4.0 | 4.5 | 5.0 |
| B | 3.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 |
| C | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 |
Tip: Always check your school’s course catalog or counselor guide — not all schools use the same weighting system.
100-Point Scale (Percentage-Based)
Some schools use a percentage system, especially in progress reports or transcripts. To convert a percentage to GPA:
| Percent Range | GPA Equivalent |
|---|---|
| 90–100% | 4.0 |
| 80–89% | 3.0 |
| 70–79% | 2.0 |
| 60–69% | 1.0 |
| Below 60% | 0.0 |
Many colleges will convert these scores to a 4.0 scale when reviewing applications.
Want a fun way to improve your grades and make money?
Helping others learn can seriously boost your own GPA.
Learn more here: Online Tutoring Jobs for Teens
When GPA Types Matter Most
Different GPA types—weighted, unweighted, and cumulative—can affect your academic future in different ways:
College Admissions
- Colleges usually recalculate your GPA using their own scale, often ignoring weighting or retaking policies.
- Some competitive schools consider both weighted GPA (to reward rigor) and unweighted GPA (to compare across applicants).
Scholarships
- Merit-based programs often list a minimum unweighted GPA (e.g., 3.5 or higher).
- Honors/AP weighting may help you stand out in competitive pools.
Transcripts & Class Rank
- Cumulative GPA is shown on your transcript and is used to determine class rank, honors graduation, or eligibility for programs like NHS.
✅ Pro tip: Always know what kind of GPA a college, scholarship, or program is asking for—they don’t all want the same thing.
Struggling with your GPA? Learn how to improve it before the semester ends. Take action now—boost your GPA before it’s too late!
If you’re applying for federal aid, double-check your FAFSA accuracy too — these FAFSA mistakes can reduce your chances of getting funding.
Weighted vs. Unweighted GPA: What’s the Difference?
Not all GPAs are created equal. Most high schools calculate two types: unweighted GPA and weighted GPA. Here’s what you need to know—and how colleges view both.
🔹 What Is an Unweighted GPA?
An unweighted GPA is based on a 4.0 scale where all classes are treated equally—whether it’s AP Calculus or standard Algebra I.
| Letter Grade | Unweighted GPA (4.0 scale) |
|---|---|
| A | 4.0 |
| B | 3.0 |
| C | 2.0 |
| D | 1.0 |
| F | 0.0 |
✅ Best for: A quick snapshot of how well you’re doing overall—without factoring in course difficulty.
Tip: You can convert letter grades like A– or B+ using our Letter to GPA Converter.
🔸 What Is a Weighted GPA?
A weighted GPA gives extra points for harder classes, like AP, IB, or honors courses. It’s usually based on a 5.0 scale, rewarding academic challenge.
| Letter Grade | Standard Class | Honors Class | AP/IB Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 4.0 | 4.5 | 5.0 |
| B | 3.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 |
| C | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 |
| D | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 |
| F | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
Pro tip: If your school offers weighted classes, it can help your GPA exceed 4.0—which looks great on competitive college applications. Try it out using our free GPA calculator tool to compare your weighted and unweighted GPA.
You can also explore our dedicated AP GPA calculator if you’re taking multiple Advanced Placement courses.
⚖️ Weighted vs. Unweighted GPA: Side-by-Side
| Aspect | Unweighted GPA | Weighted GPA |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | 0.0 to 4.0 | 0.0 to 5.0 (varies by school) |
| Class difficulty | Not factored in | Extra credit for AP, IB, Honors |
| Fairness | Equal across all students | Rewards advanced coursework |
| Max GPA possible | 4.0 | Often 4.5–5.0 |
| Used by colleges | Many recalculate to 4.0 | Still reviewed to assess rigor |
For more detail comparison read our guide Weighted or Unweighted GPA.
Do Colleges Prefer Weighted or Unweighted GPA?
Both matter.
- Colleges recalculate your GPA using their own formulas—often based on your cumulative GPA—but they also consider the rigor of your course load.
- Some top universities (like UC schools) cap the weighted GPA at 8 semesters of honors/AP classes.
- Your high school profile (sent with your transcript) helps colleges interpret your GPA in context.
Check Your School’s Policy
Weighting systems aren’t universal. Some schools use:
- 4.0, 4.5, or 5.0 scales
- Caps on how many classes are weighted
- Different weights for AP vs IB vs dual enrollment
Tip: Ask your guidance counselor or review your school’s course catalog to confirm how GPA is calculated. If you’re planning summer coursework or AP classes, check out our summer prep for high school students guide to help you plan strategically.
GPA Calculators for High School and College Students
Our user-friendly GPA calculators are designed to help you determine both unweighted and weighted GPAs, factoring in the specific details of your coursework. Utilize the tools below to gain a clearer understanding of your academic standing and identify areas for improvement as you work toward your academic objectives.
Unweighted GPA Calculator
Weighted GPA Calculator
Use other tools and calculators: Important Tools & Calculators for Students and Parents.
What is a Good GPA? Comparing College & Career Benchmarks
A good GPA depends on your goals. Here’s a benchmark for different opportunities:
| GPA | Competitive For |
|---|---|
| 3.5 – 4.0+ | Ivy League & top universities, merit scholarships |
| 3.0 – 3.5 | Mid-tier colleges, some scholarships |
| 2.5 – 3.0 | Community colleges, trade schools |
| Below 2.5 | Limited college options, focus on improvement |
Didn’t get the score you were hoping for? You’re not stuck. 👉 Explore your AP retake options before it’s too late.
The Impact of GPA on Your Academic and Career Goals
Your GPA is more than just a number—it’s a critical tool that shapes your future in academics and beyond. Whether you’re a high school student eyeing top colleges or a college student aiming for career opportunities, GPA plays a major role in opening doors.
Why GPA Matters
- Academic Standing: Your GPA reflects your overall performance in school. A strong GPA can earn you a spot on the honor roll or keep you eligible for competitive programs.
- Scholarships: Many scholarships use GPA as a key factor to decide who gets awarded. For example, a merit-based scholarship might require a minimum GPA of 3.5.
- Honors Societies: Prestigious groups like the National Honor Society often require a high GPA for membership, boosting your resume and academic credibility.
- Career Opportunities: Some employers and internship programs consider GPA when screening applicants, as it indicates discipline, time management, and consistency.
For instance, if you’re applying for a scholarship, a 4.0 GPA might automatically put you on the shortlist. Similarly, companies hiring interns often give preference to students with strong academic records.
In some cases, students may have the option to take a pass/fail grading system, which can impact their GPA in different ways.
How Colleges Use GPA in Admissions
Colleges evaluate GPA alongside other factors like extracurriculars and test scores to gauge a student’s potential. The chart below highlights the weight of each component in the admissions process.
Pie chart showing GPA (40%), extracurriculars (30%), test scores (20%), and essays (10%) as key factors in college admissions.

Colleges see GPA as a reflection of your dedication and ability to handle academic challenges. However, they don’t look at GPA in isolation. It’s often evaluated alongside your extracurricular activities, recommendation letters, and test scores like the SAT or ACT.
For example:
- A student with a slightly lower GPA but outstanding extracurricular achievements might still stand out to admissions officers.
- Conversely, a perfect GPA can strengthen your case if other areas, like test scores, are average.
Admissions officers also consider the context of your GPA. Did you take challenging AP or IB courses? Did your GPA improve significantly over time? These factors can showcase your growth and resilience.
Learn how to keep stress in check while aiming for a strong GPA with AP exams.
Action Plan to Raise Your GPA
Improving your GPA isn’t just about studying harder—it’s about studying smarter. With the right strategies, you can maximize your academic potential and see real results. Whether you’re aiming for college admissions, scholarships, or personal growth, these tips will help you stay on track.
Mastering Time Management
Balancing school, extracurriculars, and personal life can be overwhelming. Use a planner or digital calendar to schedule study sessions, assignments, and exams. Prioritize difficult subjects when your energy levels are highest, and break tasks into manageable chunks.
Developing Effective Study Habits
- Find a quiet, distraction-free study environment.
- Use active learning techniques like summarizing notes or teaching concepts to others.
- Take regular breaks using the Pomodoro Technique (25-minute focus sessions with short breaks).
- Form study groups to reinforce learning and clarify doubts.
Seeking Help When Needed
Don’t hesitate to ask teachers for clarification or attend tutoring sessions. Online resources, like Khan Academy or school-provided study guides, can also be valuable tools.
Using Extra Credit Opportunities Wisely
Extra credit can give your GPA a much-needed boost, but it’s important to use it strategically. Rather than relying on it last-minute, take advantage of opportunities throughout the semester. Look for bonus assignments, participate in class discussions, and submit optional projects when available.
Checklist: GPA Improvement Tips
✅ Create a study schedule and stick to it.
✅ Prioritize difficult subjects early in the day.
✅ Take effective notes and review them regularly.
✅ Use extra credit assignments to boost your grade.
✅ Seek help from teachers, tutors, or study groups.
✅ Avoid last-minute cramming—consistency is key!
Stay consistent, stay motivated, and watch your hard work pay off! If you’re struggling with your grades, here are effective strategies to improve your GPA in high school and college.
Frequently Asked Questions About GPA
✅What is a good GPA?
A good GPA depends on your goals. For college admissions, a 3.5 or higher is typically considered strong. Competitive scholarships and programs may look for GPAs above 3.7, while a 4.0 is often ideal for top-tier schools.
✅How is GPA used in scholarships?
GPA is a key factor for merit-based scholarships. Many programs set minimum GPA requirements (e.g., 3.0 or 3.5) to determine eligibility. A high GPA shows academic commitment, which can give you an edge over other applicants.
✅What’s the difference between overall and cumulative GPA?
Overall GPA: The average of all grades earned during your entire academic career.
Cumulative GPA: The average of grades earned during a specific period, like a semester or year.
Both are important, but overall GPA often holds more weight for long-term goals like college applications.
✅ What is a competitive GPA for college?
Most top universities require a 3.5+ GPA, while state schools may accept 2.5 – 3.0.
✅ Does GPA matter for jobs?
For competitive fields (finance, law, medicine), a high GPA (3.5+) can help. In other industries, experience and skills matter more.
✅ What is the GPA scale in high school?
High schools typically use a 4.0 scale, but some offer a 5.0 scale for advanced courses.
✅ How does the GPA scale vary by country?
The U.S. uses a GPA system, while other countries use percentage-based or letter grades (e.g., UK: First-Class, Canada: A/B/C).
Related Posts You Might Like
What Is Cumulative GPA and How to Calculate It
A deep dive into how your long-term GPA is computed and why it matters.
Top Free Grade Calculator Tools for Students & Teachers
Accurately track your performance with calculators designed for GPA, final grades, and more.

Nawab, an educator teaching K-12 since 2010, holds an English honors graduate degree and a diploma in elementary education. He has also been blogging for five years, sharing insights for educators and parents.

